Fields of application
Purpose 1
It is suitable for vitamin B1 deficiency, has the function of maintaining normal glucose metabolism and nerve conduction, and is also used for the adjuvant treatment of dyspepsia and neuritis
Preparation method:
Method 1
Thiamine hydrochloride is usually obtained by condensation, hydrolysis, neutralization, oxidation, and acidification of excess acetamidine hydrochloride with α-dimethoxy β-methoxypropionitrile.
Upstream and downstream product information
Upstream raw materials
Ethanol, hydrogen peroxide, dimethyl sulfate, ethyl chlorosulfonate, acrylonitrile, carboxylate, alpa-acetyl-gama-butyl ester
Downstream products
Sulfadiazine, 4-amino-2-methylpyrimidine-5-carboxaldehyde, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran-3-ketofurfural, 4-methyl-5-(beta-hydroxyethyl)thiazolethiamine, thiocyanate
Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)
MSDS info Thiamine chloride(59-43-8).msds
List of frequently asked questions
Brief introduction
Vitamin B1, also known as "thiamine" and "thiamine", is one of the B vitamins. It promotes normal glucose metabolism and is necessary for the normal function of nerve conduction, heart and gastrointestinal tract. It combines with adenosine triphosphate to form vitamin B1 pyrophosphate (thiamine diphosphate, i.e., conuclase), which is a necessary coenzyme for carbohydrate metabolism, and the deficiency of this coenzyme can lead to the formation of pyruvate and lactic acid accumulation due to the obstruction of oxidative metabolism, affecting the body's energy supply. Vitamin B1 also inhibits cholinesterase activity when deficient; Cholinesterase activity is enhanced, acetylcholine hydrolysis is accelerated, leading to nerve impulse conduction disorders, affecting gastrointestinal and myocardial function.
Vitamin B1
Physicochemical properties
Vitamin B1 is a white fine crystal or crystal powder, melting point 248 °C (decomposition), very soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ether, benzene, chloroform, soluble in propylene glycol.
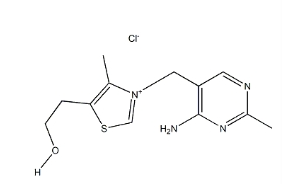
Vitamin B1 structure
Figure 1 shows the structural formula of vitamin B1.
Food sources
Vitamin B1 is abundant in seed rind and germ, such as rice bran, wheat bran, etc.; The content in coarse grains is higher than in refined rice or white flour. Others such as yeast, lean meat, peanuts, soybeans, liver, whole wheat, fresh fruits and vegetables such as cabbage, celery, spinach, bananas, oranges, grapes, traditional Chinese medicine parsnip, psyllium, coix seeds are rich in vitamin B1. Now the medicinal vitamin B1 is a synthetic thiamine hydrochloride.

Related News
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible