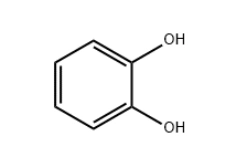
Method 1
Its preparation methods are as follows:
2,4-disulfophenol alkali melt hydrolysis method;
o-chlorophenol hydrolysis;
phenol direct oxidation;
phenolic oxidation;
O-hydroxycyclohexanone dehydroaromatization.
Among them, (1) and (2) the process is complex, the three wastes are polluted, and they are gradually replaced by new processes, while methods (4) and methods (5) are being industrialized abroad. The phenol direct oxidation method uses hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant, and the hydroxylation reaction directly occurs in the ortho and para positions of phenol in the presence of a catalyst, and the method has achieved great success after entering the 70s of the 20th century. In 1973, the French Rhône-Planck company built a set of catechol 10800t/a and hydroquinone 7200t/a industrial plant, and Japan's Utoko Industrial Company also built a set of 600t/a catechol plant. The direct oxidation method has become the easiest method for the production of catechol, and methyl isobutyl ketone is used as an extractant to extract and separate o-, hydroquinone and unreacted phenol.
The process is made by direct oxidation of phenol and hydrogen peroxide.
This method has been industrialized abroad, and in recent years at home.
Phenol and methyl ethyl ketone, 60% H2O2 and activated clay VH and 85% H3PO4 were added to the reactor, and phenol was converted into catechol and hydroquinone by stirring at 100 °C for 30min.
Method two
Catechol is mostly found in nature in the form of derivatives. For example, o-methoxyphenol and 2-methoxy-4-methylphenol are important components of beech creosote oil. Catequinone was first obtained by distilling protocatechuic acid or distilling catechu extract: later it was found that catechol could also be obtained by dry distillation of certain plants or alkali melting of certain resins. In the past, it was generally extracted from tar from low-temperature dry distillation of coal. There are various process routes for the synthesis of catechol. (1) Phenol is used as raw material, and it is obtained by chlorine chlorination, copper sulfate and sodium hydroxide hydrolysis, and hydrochloric acid acidification. (2) It is directly oxidized by benzene or phenol and hydrogen peroxide. The use of hydrogen peroxide direct oxidation of phenol to produce catechol includes Japan's Ube Industries Company and France's Rhône-Planck Company. (3) It is prepared by hydrolysis of o-chlorophenol under pressure in an alkaline medium.

Related Products
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible
Related News
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible