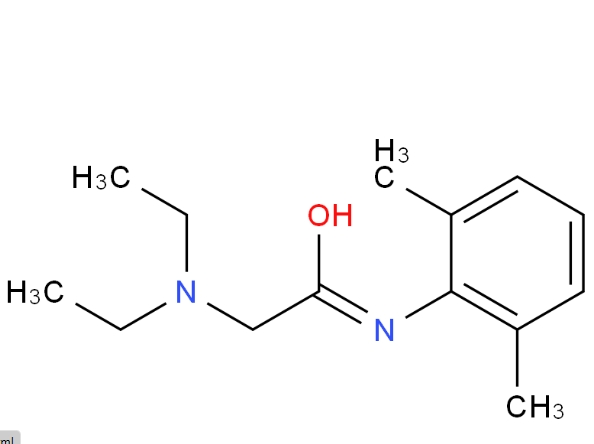
Lidocaine
Chinese name: Lidocaine
Chinese aliases: N-diethylaminoacetyl-2,6-dimethylaniline; N-Diethylacetyl-2,6-dimethylaniline; 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide.
English name: lidocaine
English alias: L-Caine; Leostesin; 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide; Esracaine; 2-diethylamino-2',6'-acetoxylidide;
CAS number: 137-58-6
Molecular Formula: C14H22N2O
Molecular Weight: 234.337
Exact Mass: 234.17300
PSA:32.34000
LogP:2.65670
Physical and chemical properties
Appearance and properties: white crystalline powder
Density: 0.9944 g/cm3
Melting point: 66-69 °c
Boiling point: 372.7ºC at 760mmHg
Flash point: 179.2ºC
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidants.
Storage conditions: Store in a cool and dry place. Keep the container closed when not in use.
Vapour pressure: 4.28E-05mmHg at 25°C
Pharmacology and toxicology
This product is an amide local anesthetic. After blood absorption or intravenous administration, it has obvious excitation and inhibition biphasic effect on the central nervous system, and there can be no precursor excitement, when the blood concentration is low, analgesia and drowsiness, and the pain threshold is increased; With the increase of dose, the effect or toxicity increases, and there is an anticonvulsant effect at the concentration of subtoxic blood drugs; When the blood concentration exceeds 5 mg·mL-1, convulsions can occur. At low doses, this product can promote the outflow of K+ in cardiomyocytes, reduce the auto-discipline of myocardium, and have anti-ventricular arrhythmic effect; At therapeutic doses, there is no significant effect on the electrical activity of cardiomyocytes, atrioventricular conduction and contraction of myocardium; Further increase in blood concentration can cause slowing of cardiac conduction velocity, atrioventricular block, inhibition of myocardial contractility and decrease of cardiac output.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral bioavailability is low, and the first hepatic effect is sharply reduced. Absorbed completely after intramuscular injection. After absorption, it quickly distributes into the heart, brain, kidneys and other tissues rich in blood supply, and then distributes to fat and muscle tissue. The apparent volume of distribution is about 1 L/kg, and the volume of distribution is reduced in heart failure. The protein binding rate is about 51%. Smokers can have higher rates of binding than non-smokers.
It takes effect 5~15 minutes after intramuscular injection, and reaches the therapeutic concentration in 15~20 minutes after a intramuscular injection of 200mg, lasting 60~90 minutes;
It takes effect immediately after intravenous injection (about 45~90 seconds) and lasts for 10~20 minutes. The therapeutic plasma concentration is 1.5~5μg/mL, and the poisoning blood concentration is more than 5μg/mL. Continue intravenous drip for 3-4 hours to reach steady-state blood concentration, acute myocardial infarction takes 8~10 hours. 90% metabolized by the liver, metabolites monoethylglycylxylxylaniline (MEGX) and glycylxylbenzilide (GX) have pharmacological activity, continuous intravenous drip for more than 24 hours, metabolites can produce therapeutic and toxic effects. The half-life after intravenous injection α about 10 minutes, and the β is about 1~2 hours. The GX half-life is about 10 hours longer, and the MEGX half-life is similar to that of the original drug. Patients with heart failure, liver disease, the elderly and continuous intravenous drip for more than 24~36 hours, the clearance of this product is slowed down. Excreted by the kidneys, 10% as the original drug, 58% as metabolites (GX), can not be removed by hemodialysis.
The efficacy and duration of local anesthesia of lidocaine are stronger than that of procaine, but the toxicity is also greater. The deethyl metabolite (monoethylglycinamide xylene) metabolized in the liver still has local anesthetic properties, increases toxicity, and is further degraded by amidase and excreted with urine, and 10% of the dosage is excreted in its original form.
Clinical application
It is suitable for acute ventricular arrhythmias caused by acute myocardial infarction, surgery, digitalis poisoning and cardiac catheterization, including ventricular premature beats, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. Secondly, it is also used for status epilepticus who does not respond to other anticonvulsants and local or neuraxial anesthesia. It can also relieve tinnitus.


Related News
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible