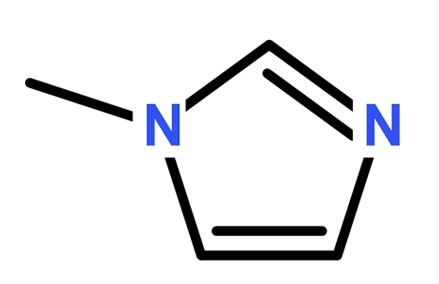
1H-imidazole
Melting point 88-91 °C (lit.) Boiling point 256 °C (lit.) Density 1.01g/mLat20 °CVapor pressure< 1mmHg (20 °C) Refractive index 1.4801Flash point 293 °F Storage conditions StChemicalbookorebelow+30 °C. Solubility H2O: 0.1Mat20 °C, clear, colorless morphology, crystalline acidity coefficient (pKa) 6.953 (at25 °C)
Imidazole, molecular formula C3H4N2, is an organic compound, a type of diazole, a five-membered aromatic heterocyclic compound containing two meta-nitrogen atoms in its molecular structure. The unshared electron pair of the 1-position nitrogen atom in the imidazole ring participates in the cyclic conjugation, and the electron density of the nitrogen atom decreases, making the hydrogen on this nitrogen atom easy to leave as hydrogen ions.
Imidazole is acidic, also alkaline, can form salts with strong bases, the chemical properties of imidazole can be summarized with the synthesis of pyridine and pyrrole, these two structural units precisely in the enzyme histidine as an acyl transfer reagent in the catalysis of lipid hydrolysis plays an important role. Derivatives of imidazole exist in the biological organism and are more important than imidazole itself in scientific research and industrial production, such as DNA, hemoglobin, etc.
The electron cloud density on imidazole N-3 is large, so alkylation usually occurs first on this nitrogen atom. The product of a single alkylation can produce a nitrogen atom similar to that in pyridine through tautomerization, so it can be further reacted to produce the product of dialkylation imidazolium salt.
The acylation reaction of imidazole generally occurs on N-3, but because the acyl group is an electron-absorbing group, the reaction can be controlled in the monoacylation stage, and the product is N-acylimidazole.
The active hydrogen of imidazole can decompose Grignard's reagent to form the N-magnesium salt of imidazole, which is isomerized to obtain C-2-substituted imidazole. The latter is treated with methyl iodide to produce 1,2-dimethylimidazole.
Imidazole can be added to the diolenophile, forming a 3-amium amphoteric ion, and then adding with another molecule of the diene nucleophile to form a product of C-2 cyclization. For example, 1-methyl-2-ethylimidazole reacts with two molecules of dimethyl butynedioate to obtain 4methyl 8α-ethyl-1-methyl-1,8α-dihydroimidazol[1,2-a]pyridine-5,6,7,8-tetracarboxylate.


Related Products
Related News
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible