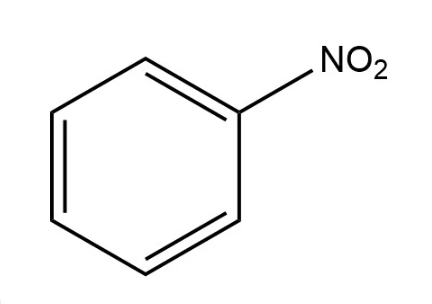
CAS 98-95-3
Chinese name nitrobenzene
Foreign name Nitrobenzene
Chemical formula C6H5NO2
Molecular Weight: 123.109CAS
Registration number: 98-95-3EINECS
Registration number 202-716-0
Boiling point 210 to 211 °C
Water solubility, difficult to dissolve in water
Density 1.205 g/cm³
Flash point 88 °c
Security Description S7; S16; S27; S28; S36/37;S45; S61 Hazard symbol T; N
Chinese name nitrobenzene
English name nitrobenzene
English aliases more
Nitrobenzene physicochemical properties
Density 1.205
boiling point 210-211 °C(lit.)
melting point 5-6 °C(lit.)
Molecular Formula C6H5NO2
Molecular Weight: 123.10900
Flash point 190 °F
Exact mass 123.03200
PSA 45.82000
LogP 2.11800
Appearance traits yellow liquid
Vapor density 4.2 (vs air)
Vapour pressure 0.15 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
refractive index n20/D 1.551(lit.)
Storage conditions
Storage precautions Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from tinder, heat sources. Keep the container tightly sealed. It should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, alkalis, and edible chemicals, and mixed storage should be avoided. Equipped with fire fighting equipment of corresponding varieties and quantities. Storage areas should be equipped with emergency treatment equipment for leakage and suitable containment materials.
stability
1. Chemical properties: relatively stable to acids and alkalis. It can volatilize with water vapor and has weak oxidation. Iron, zinc and other metals react with hydrochloric acid, or use nickel, copper, silver, etc. as catalysts, pressure for reduction, to generate aniline. React with the mixed acid of sulfuric acid and nitric acid to generate dinitrobenzene or trinitrobenzene. Chlorination is carried out in the presence of iodine or magnesium chloride to form m-clonitrobenzene. The chlorination reaction is carried out in the presence of ferric chloride, and 2,5-dichloronitrobenzene is formed at room temperature. At 100 °C, 2,3,5,6-tetrachloronitrobenzene is generated. HCB is generated above 100 °C. The interaction with oleum sulfuric acid mainly produces m-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid. It reacts with potassium hydroxide to form o-nitrophenol and a small amount of p-nitrophenol. Nitrobenzene can react with Grignard's reagent.
2. Stability Stable
3. Forbidden substances strong oxidants, ammonia, amines, etc
4. Aggregation hazards do not polymerize
5. Decomposition products nitrogen oxides


Related Products
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible
Related News
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible