melting point:248 °C (decomp)
Density1.3175 (rough estimate)
refractive index1.5630 (estimate)
Storage conditionsKeep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature
Solubility DMSO : 6 mg/mL (19.95 mM)
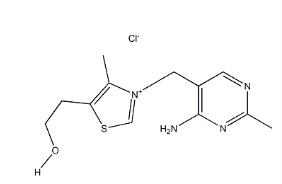
InChIInChI=1S/C12H17N4OS. ClH/c1-8-11(3-4-17)18-7-16(8)6-10-5-14-9(2)15-12(10)13; /h5,7,17H,3-4,6H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,14,15); 1H/q+1; /p-1
InChIKeyMYVIATVLJGTBFV-UHFFFAOYSA-M
SMILESO([H])CCC1=C(C)[N+](=CS1)CC1C=NC(=NC=1N)C.[Cl-]
LogP-3.930 (est)
CAS DataBase Reference: 59-43-8 (CAS DataBase Reference)
EPA Chemical Information Thiamine (59-43-8)
Vitamin B1, also known as "thiamine" and "thiamine", is one of the B vitamins. It promotes normal glucose metabolism and is necessary for the normal function of nerve conduction, heart and gastrointestinal tract. It combines with adenosine triphosphate to form vitamin B1 pyrophosphate (thiamine diphosphate, i.e., conuclase), which is a necessary coenzyme for carbohydrate metabolism, and the deficiency of this coenzyme can lead to the formation of pyruvate and lactic acid accumulation due to the obstruction of oxidative metabolism, affecting the body's energy supply. Vitamin B1 also inhibits cholinesterase activity when deficient; Cholinesterase activity is enhanced, acetylcholine hydrolysis is accelerated, leading to nerve impulse conduction disorders, affecting gastrointestinal and myocardial function.

Related Products
Related News
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible